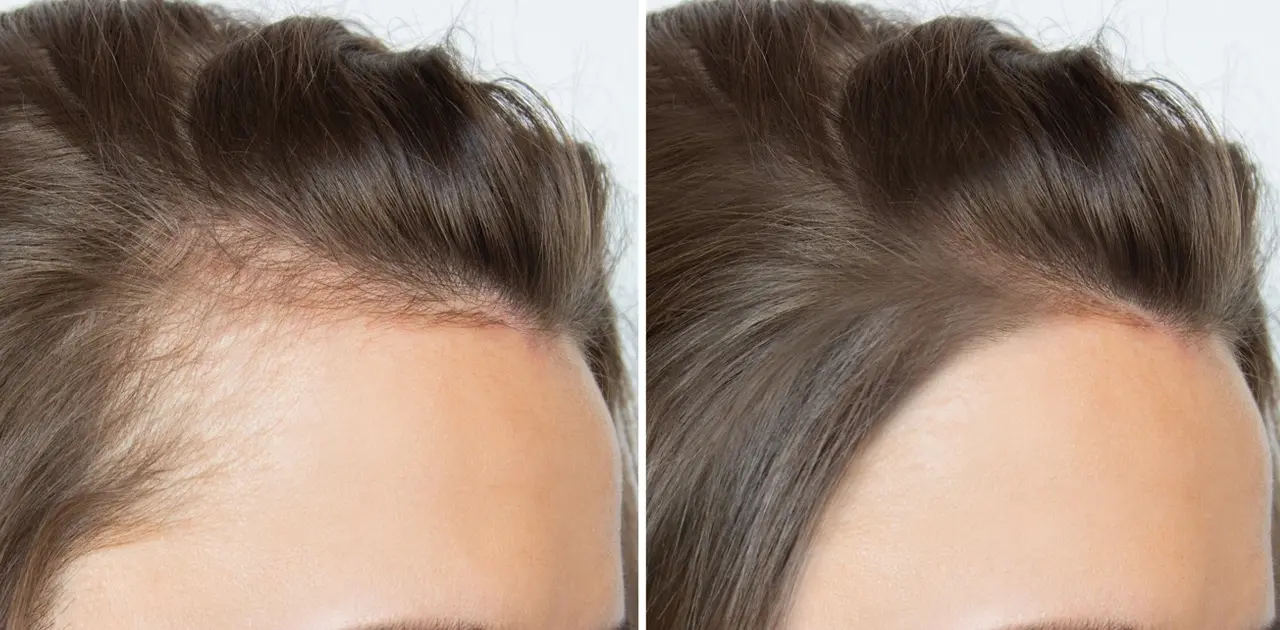
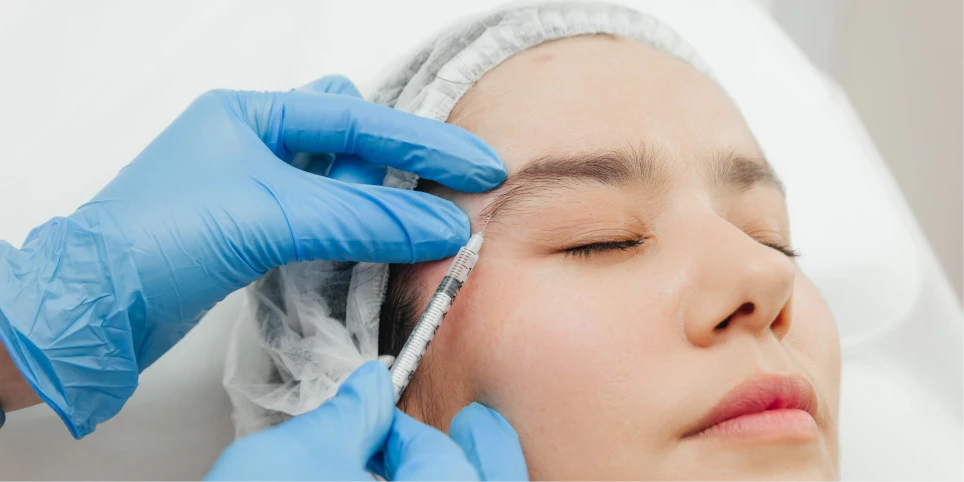
Botox is a name synonymous with cosmetic enhancement, primarily used to smooth wrinkles and give individuals a more youthful appearance. However, this powerful neurotoxin has been found to offer a plethora of medical benefits that go beyond aesthetic improvements. Recent advances in medical research have showcased how Botox can be used to alleviate a variety of medical conditions such as migraines and hyperhidrosis. This article dives deep into the non-aesthetic benefits of Botox, highlighting how it is helping people lead healthier, more comfortable lives.
Understanding Botox: A Brief Overview
What is Botox?
Botox, or botulinum toxin, is a neurotoxic protein produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. In controlled doses, it can be used safely for both cosmetic and medical treatments. When injected, it blocks nerve signals that cause muscle contractions, resulting in temporary muscle paralysis. This mechanism makes it effective not just for reducing wrinkles but also for a wide array of medical conditions.
How Does Botox Work?
By interrupting the communication between nerves and muscles, Botox prevents certain muscles from contracting. This results in the relaxation of targeted muscles for a duration of three to six months. This very property has paved the way for numerous therapeutic applications.
The Rising Popularity of Therapeutic Botox
In recent years, the therapeutic uses of Botox have gained traction. According to a report by Market Research Future, the global botulinum toxin market is set to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 10.3% from 2019 to 2025. This growth is driven largely by increased awareness of its medical applications. Below, we delve into some of the most impactful medical benefits of Botox.
Medical Benefits of Botox: Beyond Aesthetics
Botox for Migraines: A Game-Changer
The Science Behind Botox for Migraine Relief: Migraines affect over 38 million people in the United States alone, according to the Migraine Research Foundation. Chronic migraines can significantly hinder an individual’s quality of life. Botox has emerged as a promising treatment option for those who suffer from chronic migraines, defined as experiencing headaches on 15 or more days per month.
In 2010, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Botox as a treatment for chronic migraines. Clinical studies have shown that Botox can reduce the frequency of migraine days by preventing the release of certain chemicals involved in pain transmission.
How Botox is Administered for Migraines
The treatment involves injecting Botox into specific areas around the head and neck. Typically, a total of 31 injections are administered, with the injections placed in the forehead, temples, the back of the head, neck, and upper back. Patients usually see a reduction in the frequency and severity of migraines within two weeks of treatment.
Case Study: Botox Efficacy in Migraine Treatment
A study published in “Headache: The Journal of Head and Face Pain” followed 688 migraine patients treated with Botox. The majority of participants experienced a significant reduction in the number of migraine days, with many reporting a decreased reliance on other medications.
Hyperhidrosis: Sweating Out Excessive Sweating
Understanding Hyperhidrosis: Hyperhidrosis is a condition characterized by excessive sweating, affecting approximately 4.8% of the U.S. population. This condition can be socially and emotionally distressing, often causing significant impairment in daily activities.
How Botox Alleviates Hyperhidrosis
Botox helps in treating hyperhidrosis by blocking the nerve signals that activate sweat glands. Small doses of Botox are injected directly into the areas of excessive sweating, such as the underarms, hands, feet, or face. The treatment typically starts showing effects within a week and can last for up to six months.
Real-Life Example: Hyperhidrosis Treatment Success
A clinical trial conducted by Dr. David Pariser demonstrated the effectiveness of Botox in treating primary axillary hyperhidrosis (excessive underarm sweating). The study revealed that Botox reduced sweating by over 50% in more than 80% of participants, significantly improving their quality of life.
Addressing Overactive Bladder
The Impact of Overactive Bladder: Overactive bladder (OAB) is a medical condition that results in a sudden, involuntary contraction of the muscle in the wall of the bladder, leading to an urgent need to urinate. This condition affects approximately 33 million people in the United States, many of whom are women.
How Botox Can Help
Botox is an effective treatment option for an overactive bladder, especially when other treatment methods have failed. By injecting Botox into the bladder muscle, it helps to calm the overactive muscles, reducing urinary frequency and urgency. According to studies, Botox can reduce OAB symptoms by 70% to 80%, providing significant relief to patients.
Clinical Data Supporting Botox for OAB
A 2015 study published in “European Urology” followed 227 women with OAB who were treated with Botox. The results showed significant improvements in symptoms, with many participants experiencing fewer daily incontinence episodes and better overall bladder function.
Managing Spasticity: Regaining Control
What is Spasticity?
Spasticity is a condition characterized by abnormal muscle tightness due to prolonged muscle contraction, often seen in individuals with cerebral palsy, multiple sclerosis (MS), or after a stroke. This condition can make movement, posture, and balance challenging.
Botox for Treating Spasticity
Botox can be used to relieve muscle stiffness and spasms associated with spasticity. It works by blocking nerve signals that cause muscles to contract, allowing them to relax. Treatment typically involves injecting Botox into the affected muscles, and the effects can last for about three to four months.
Case Evidence of Botox in Spasticity
Research published in the “International Journal of Rehabilitation Research” observed that Botox treatments for spasticity in stroke patients reduced muscle stiffness significantly, improving mobility and quality of life for those involved.
Botox: The Future of Medical Treatment
Emerging Trends and Future Applications
Pain Management
Botox is being explored as a potential treatment for various pain conditions, including chronic neck pain and temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJ). Preliminary studies show promise, indicating that Botox could become a standard treatment for these conditions.
Mental Health
Intriguingly, recent studies are investigating the potential benefits of Botox for mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety. By reducing frowning, Botox might influence emotional feedback to the brain, possibly leading to mood improvements.
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Researchers are also studying the effects of Botox on gastrointestinal conditions such as achalasia, a disorder affecting the esophagus. Botox injections have shown promise in relaxing the esophageal muscles, improving swallowing function in patients with this condition.
Expert Opinions: What the Professionals Say
Dr. Andrew Blumenfeld, Neurologist, Headache Center of Southern California
“Botox has opened new avenues for the treatment of chronic conditions like migraines and hyperhidrosis. Its effectiveness in reducing symptoms significantly improves patients’ quality of life.”
Dr. David Pariser, Dermatologist, Eastern Virginia Medical School
“The applications of Botox in dermatology beyond aesthetic enhancement are fascinating. We’ve seen tremendous success in treating hyperhidrosis and expect further advancements in the near future.”
Conclusion:
Botox has indeed evolved beyond its cosmetic reputation, cementing its place in modern medicine as a versatile treatment for a variety of conditions. From alleviating the debilitating pain of chronic migraines to improving the lives of those suffering from hyperhidrosis and overactive bladders, the medical benefits of Botox are ever-expanding.
As ongoing research continues to uncover new applications, Botox is set to become an even more integral part of healthcare, offering relief and improved quality of life to a growing number of patients.
By shedding light on the non-aesthetic benefits of Botox, we hope to foster greater awareness and encourage individuals to explore these treatment options with their healthcare providers. As always, it is crucial to consult with a qualified medical professional to determine the most appropriate treatment for your specific condition.